Format
ESRI Shapefile
39 record(s)
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Status
Service types
Scale
panaceaKeywords
GEMET keywords
-
Medbiolitter database summarises results of scientific studies on biodiversity and marine litter interactions in the Mediterranean Sea. To this end, information is collected from different data sources, such as institutions or projects, as well as peer-reviewed publications. The main source of data currently is LITTERBASE/AWI, including only the coverage within the Mediterranean. The database currently comprises 393 records on interactions. Interaction refers to encounters between wildlife and litter items and are classified in four categories: 1) Ingestion, which is the most frequently observed interaction, followed by 2) entanglement, which affects motility, often with fatal consequences, 3) colonization, which occurs when many species settle on floating litter, and 4) others, including different types of less frequent interaction. The database includes among others the location, the type of interaction and litter, marine realm (beach, sea surface, water column, seafloor), habitat, species, whether it occurs in a marine protected area and the type in such case, as well as references to the publication from which the data are extracted. The layer is represented in different ways in the MED Biodiversity platform: 1) Marine litter and biodiversity interactions: it shows the database by type of interaction (ingestion, entanglement, colonization and other) and marine realm (pelagic or benthic). 2) Knowledge update from Nov 2008: changes in the number of records since the last update. It tries to represent the efforts of the PANACeA project to gather additional information on the Mediterranean Sea. 3) Marine litter knowledge from 1988 to 2019: shows the years of publication of the source of the records in the database. In recent dates, especially since 2015, there has been a notable increase in the number of publications related to marine litter.
-
Medbiolitter database summarises results of scientific studies on biodiversity and marine litter interactions in the Mediterranean Sea. To this end, information is collected from different data sources, such as institutions or projects, as well as peer-reviewed publications. The main source of data currently is LITTERBASE/AWI, including only the coverage within the Mediterranean. The database currently comprises 393 records on interactions. Interaction refers to encounters between wildlife and litter items and are classified in four categories: 1) Ingestion, which is the most frequently observed interaction, followed by 2) entanglement, which affects motility, often with fatal consequences, 3) colonization, which occurs when many species settle on floating litter, and 4) others, including different types of less frequent interaction. The database includes among others the location, the type of interaction and litter, marine realm (beach, sea surface, water column, seafloor), habitat, species, whether it occurs in a marine protected area and the type in such case, as well as references to the publication from which the data are extracted. The layer is represented in different ways in the MED Biodiversity platform: 1) Marine litter and biodiversity interactions: it shows the database by type of interaction (ingestion, entanglement, colonization and other) and marine realm (pelagic or benthic). 2) Knowledge update from Nov 2008: changes in the number of records since the last update. It tries to represent the efforts of the PANACeA project to gather additional information on the Mediterranean Sea. 3) Marine litter knowledge from 1988 to 2019: shows the years of publication of the source of the records in the database. In recent dates, especially since 2015, there has been a notable increase in the number of publications related to marine litter.
-
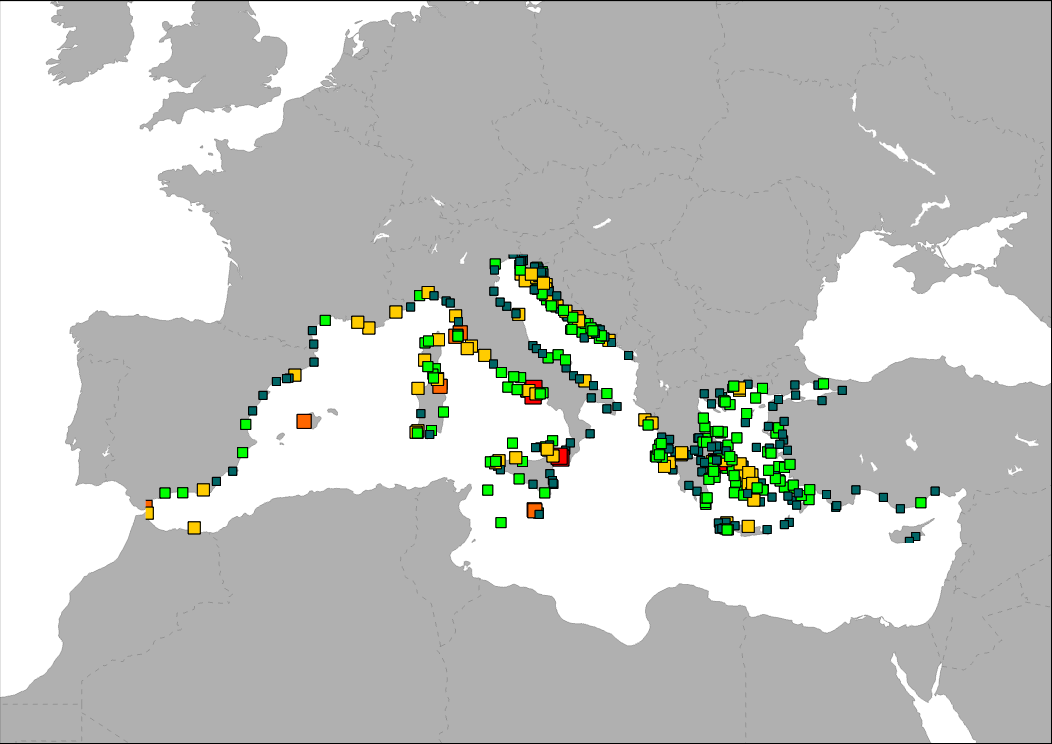
The map shows the distribution of main ferry ports in the Mediterranean Sea. Ports are classified in groups according to its level of activity.
-

The map shows the distribution of main passengers transport ports in the Mediterranean Sea. Ports are classified in groups according to its level of activity.
-
.png)
The map shows the number of moorings in marina ports per kilometre of coastline for each NUTS3 region. Data source: Plan Bleu, Spanish Yachting Port Federation, Portbooker, EEA, 2014.
-
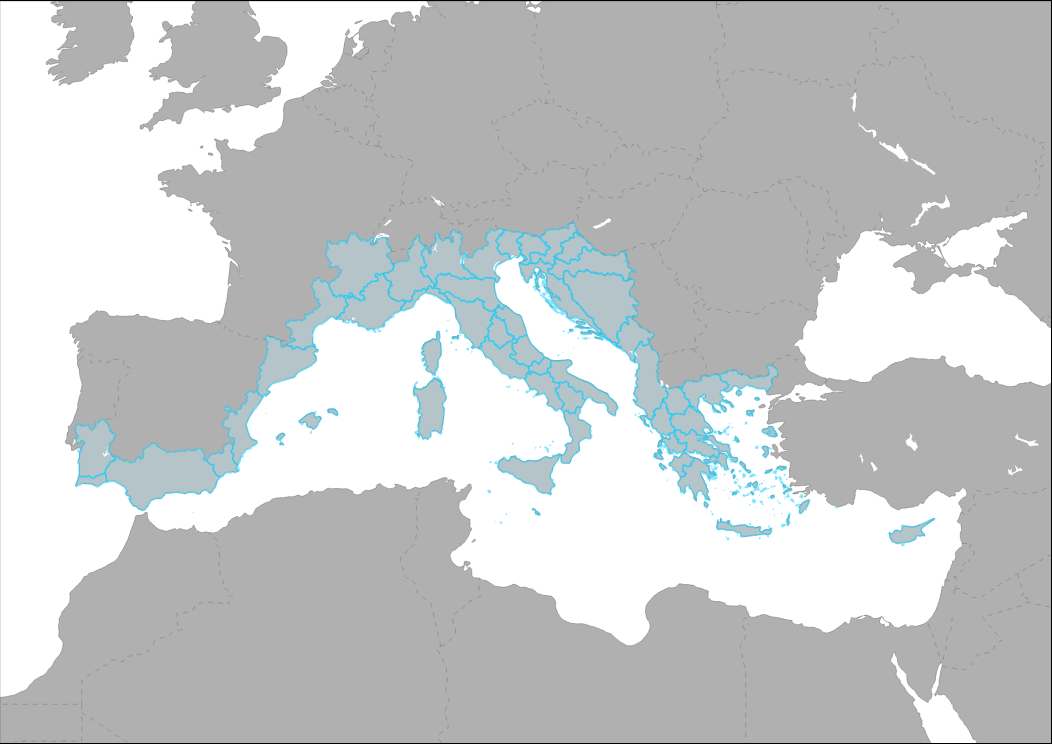
This layer represent the regions included in the MED Programme Cooperation area. It includes regions and countries in the Mediterranean Coast from Portugal to Greece and Cyprus. This list is based on the EU Commission decision of 31 October 2006 drawing up the list of eligible regions and areas for the transnational strands of the European territorial cooperation objective.
-
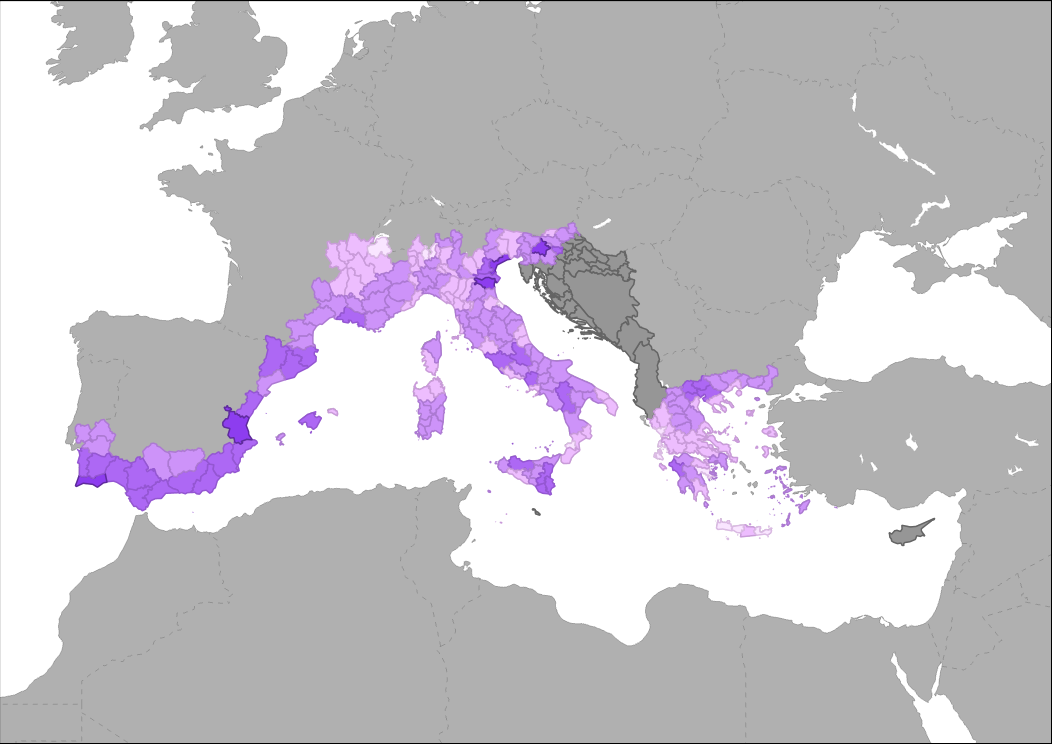
This indicator represent the pressure on coastal ecosystems due to climate change on a scale of 5 classes from very low (1) to very high (5). The assessment of climate change pressure on coastal areas correspond to ESPON Climate indicator 'Aggregate impact of climate change on Europe’s regions'. It is based on a weighted combination of physical, environmental, social, economic and cultural potential impacts of climate change.
-
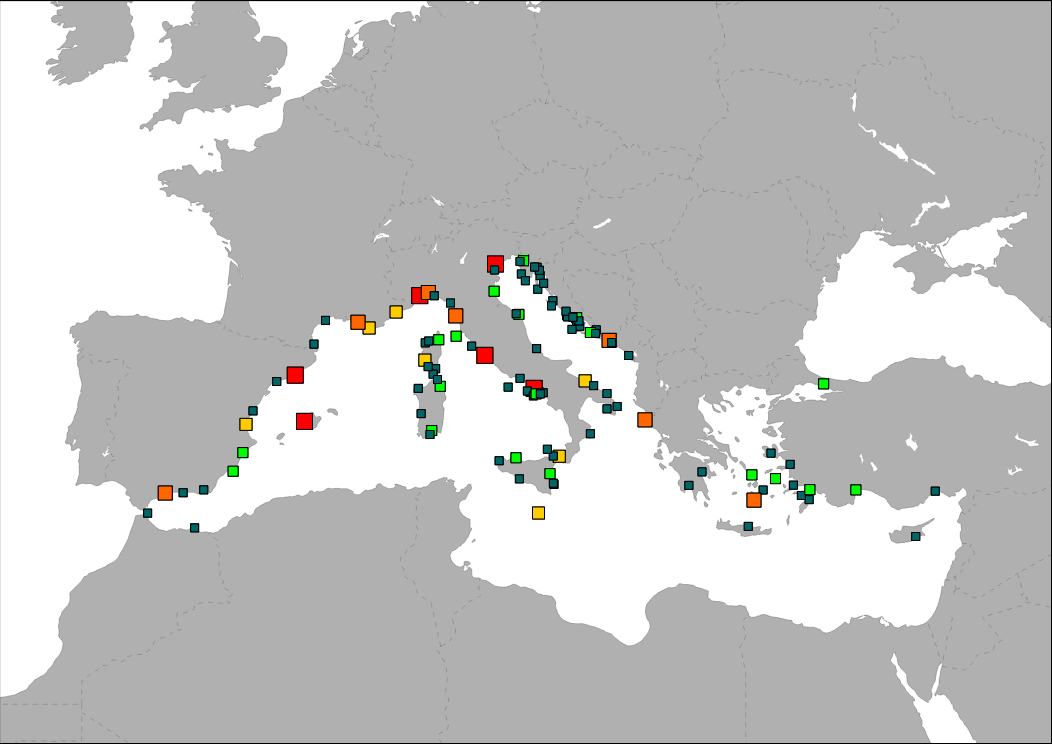
The map shows the distribution of main cruise ports in the Mediterranean Sea. Ports are classified in groups according to its level of activity.
-
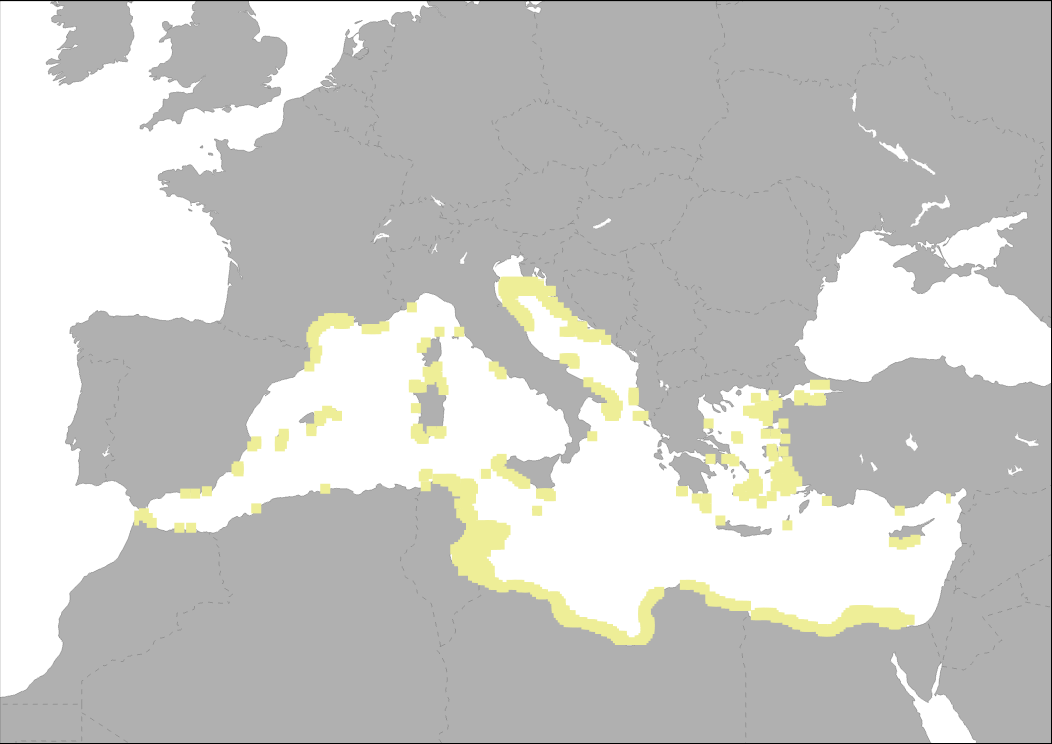
Suitable area for fixed OWF (water depth < 50 m and wind speeds*greater than 5m/sec at 80 m height above sea level) From MEDTRENDS 2015
-
Heritage is our legacy from the past, what we live with today, and what we pass on to future generations. Our cultural and natural heritage are both irreplaceable sources of life and inspiration. The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) seeks to encourage the identification, protection and preservation of cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity. This is embodied in an international treaty called the Convention concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage, adopted by UNESCO in 1972. What makes the concept of World Heritage exceptional is its universal application. World Heritage sites belong to all the peoples of the world, irrespective of the territory on which they are located. The natural marine heritage is recollected into MAPAMED which is a cartographic database of key information on Mediterranean Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) potential Other Effective área-based Conservation Measure (OECMs), and more broadly on sites of interest for marine conservation. It is developed and administered jointly by UNEP/MAP-SPA/RAC and the MedPAN Association. For detailed information, please consult the MAPAMED user manual (April 2021 version).
