Keyword
Biota
7 record(s)
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Status
Scale
Resolution
panaceaKeywords
GEMET keywords
-

Current Posidonia oceanica meadows distribution (presence points) in the Mediterranean Sea from dataset Seagrass beds distribution along the Mediterranean coasts - Mediterranean Sensitive Habitats (MEDISEH). The dataset of seagrasses distribution across the Mediterranean produced in the framework of MEDISEH derived from the compilation of published and unpublished information.
-
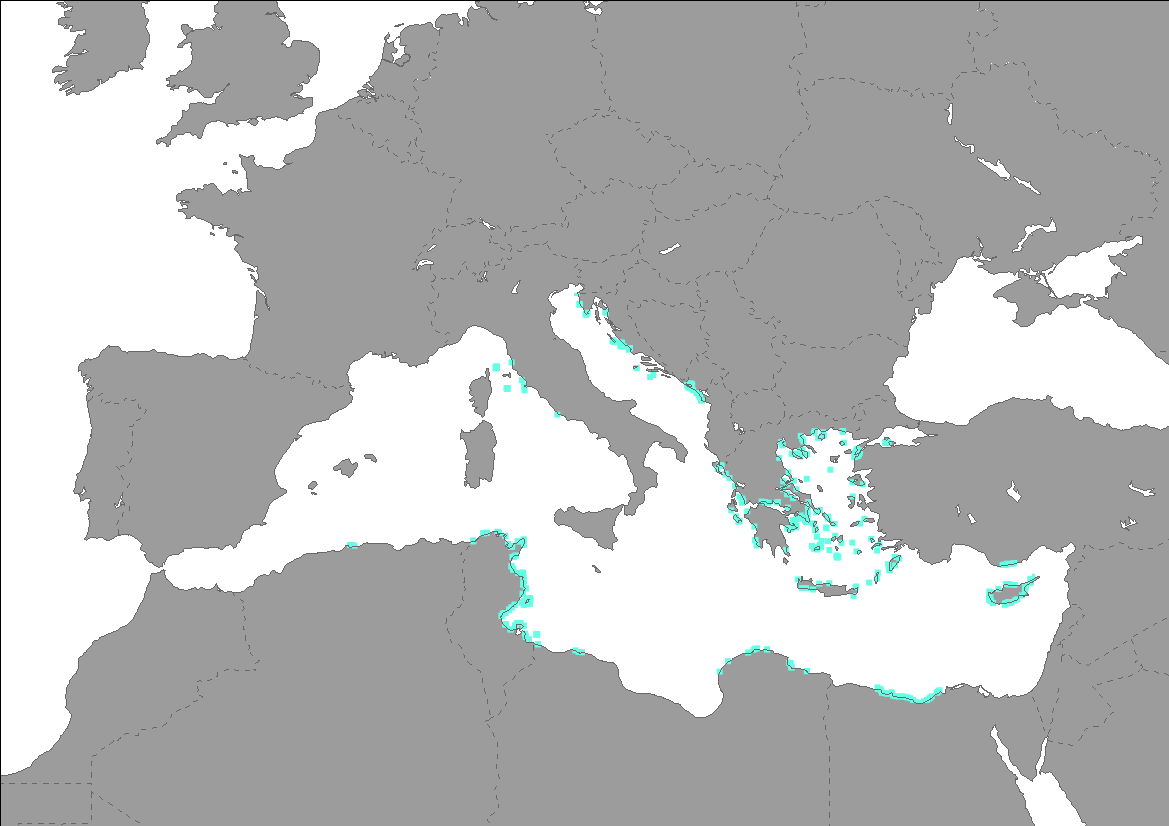
Current Posidonia oceanica meadows distribution (presence points) in the Mediterranean Sea from dataset Seagrass beds distribution along the Mediterranean coasts - Mediterranean Sensitive Habitats (MEDISEH). The dataset of seagrasses distribution across the Mediterranean produced in the framework of MEDISEH derived from the compilation of published and unpublished information. For example literature search was made using mainly the ISI Web of Knowledge engine. At the same time a new search started from the “Bibliographic References” at the end of each paper. We amended the data set with our own unpublished data (grey literature).
-
This dataset represents a data compilation of Posidonia oceanica meadows distribution along the Northern coasts of Mediterranean Sea and is composed of different subsets of point and polygon occurence data. The dataset was compiled by the Hellenic Centre for Marine Research (HCMR, Institute of Oceanography) in collaboration with the partners of the project "POSBEMED: Sustainable management of the systems Posidonia-beaches in the Mediterranean region". This dataset shows the distribution of Posidonia meadows in the spatial scale of EEA reference grid 1km. Coverage is the territory of the following EU countries: Spain, France, Italy, Croatia, Greece, Malta, and Cyprus. The dataset produced for the purposes of POSBEMED project is not exhaustive, and its careful use is recommended.
-

The data set is a secondary product accompanying the terrestrial part of the Ecosystem Type Map 2012 v3.1. It provides supplemental information: • estimated geometric reliability ranging from 1 – 10 (very low to very high) • estimated thematic reliability ranging from 1 – 10 (very low to very high) • Main original LC input data source: - Corine Land Cover - Urban Atlas - Riparian Zones - Natura 2000 (N2k) - High Resolution Layer Forest - High Resolution Layer Grassland - High Resolution Layer Imperviousness - High Resolution Layer Permanent Water Bodies - OpenStreetMap Roads - OpenStreetMap Landuse • MAES Level 2 (Urban, Cropland, Grassland, Woodland and Forest, Heathland and shrub, Sparsely vegetated land, Wetlands, Marine inlets and transitional waters)
-
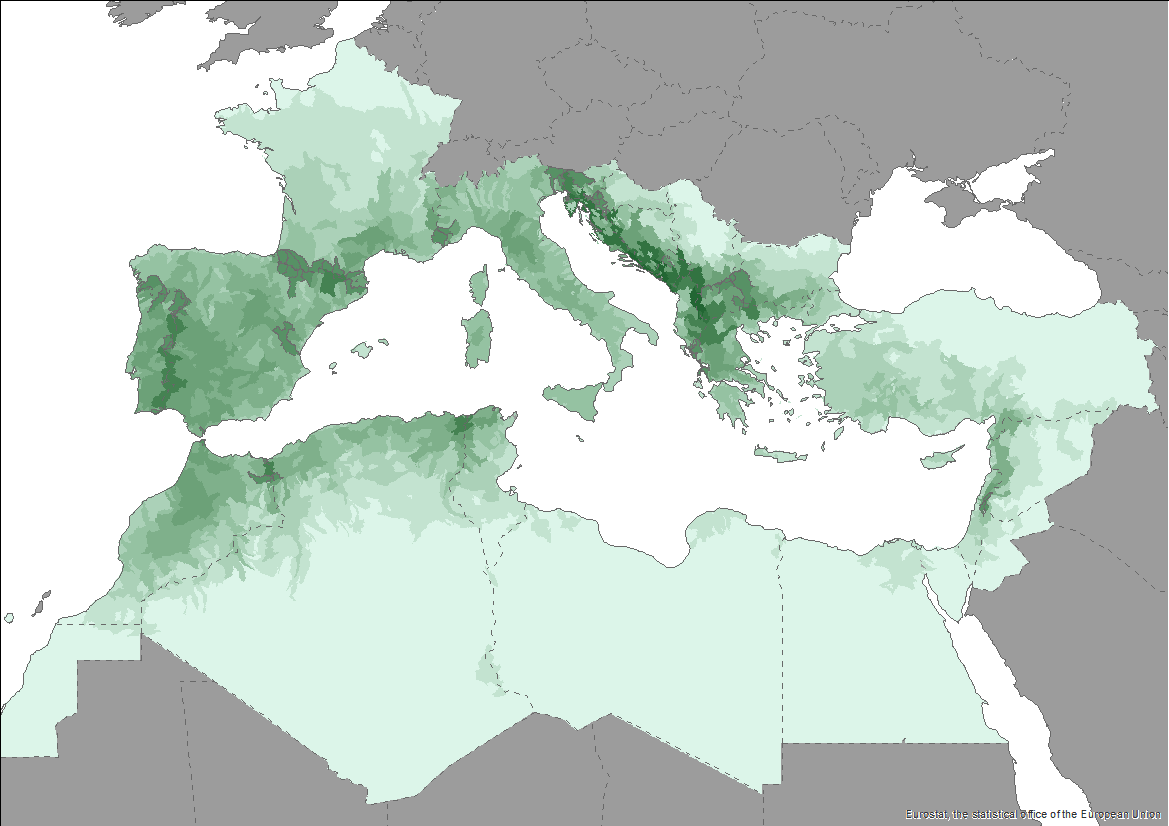
The Pan-Mediterranean wetland knowledge base builds on methods and approaches developed in the framework of on-going efforts at the Mediterranean scale to map wetland ecosystems and assess their condition. It is relevant for several on-going initiatives at a regional, European and global level (e.g. UN Decade on Ecosystem restoration, EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030, the Barcelona Convention and its protocols on Integrated Coastal Zone Management and Specially Protected Areas). As part of these efforts, ETC-UMA produced an assessment that targets the distribution, state and trends of pressures and impacts on key animal and plant biodiversity hosted by wetland habitats in the Mediterranean region. The assessment of wetland biodiversity conditions aims to complement existing knowledge and address the lack of readily available spatially-explicit information on the areas where biodiversity unique to the Mediterranean occurs, and where endemic biodiversity is most threatened, using data from The Red List of Threatened Species™ of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). For the threatened species analysis, only species categorised in the IUCN Red List as Critically Endangered (CR), Endangered (EN) and Vulnerable (VU) were considered. The goal is to highlight priority areas for potential conservation actions in the region, and to support the regional efforts in advocating for effective wetland management and nature-based solutions in the Mediterranean region.
-
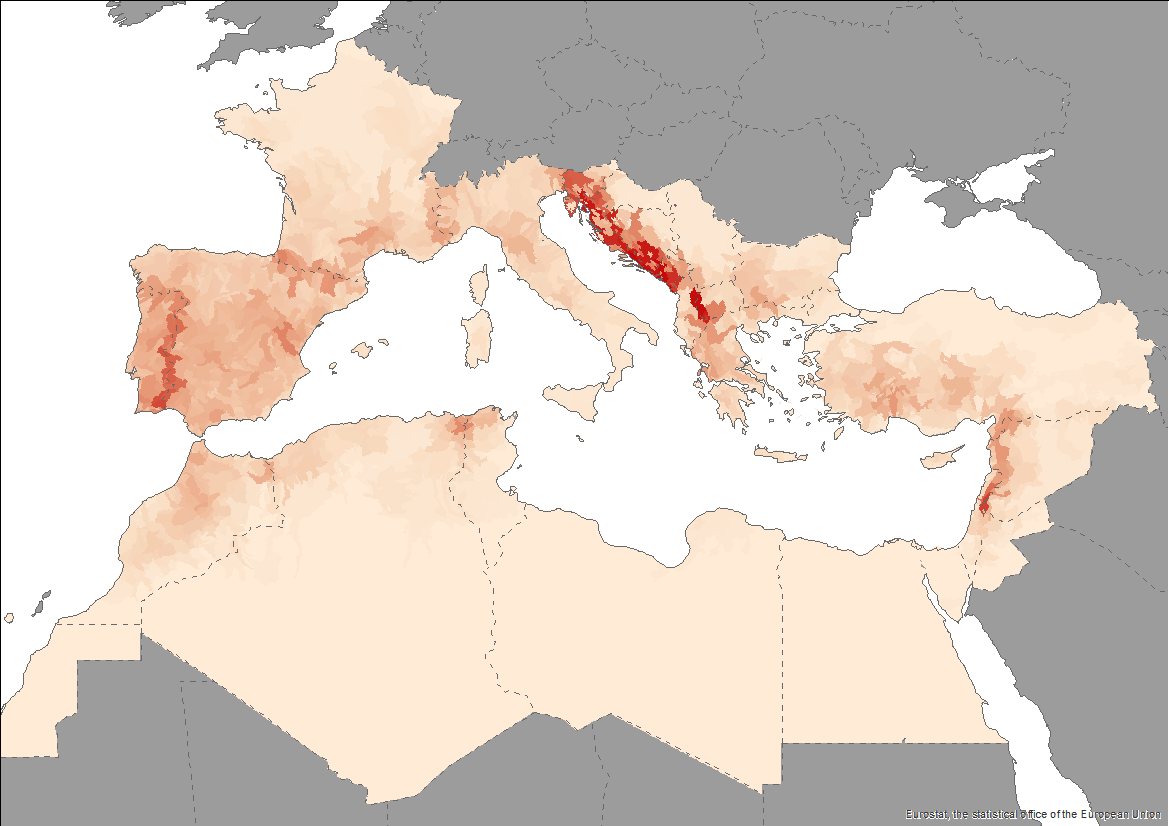
The Pan-Mediterranean wetland knowledge base builds on methods and approaches developed in the framework of on-going efforts at the Mediterranean scale to map wetland ecosystems and assess their condition. It is relevant for several on-going initiatives at a regional, European and global level (e.g. UN Decade on Ecosystem restoration, EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030, the Barcelona Convention and its protocols on Integrated Coastal Zone Management and Specially Protected Areas). As part of these efforts, ETC-UMA produced an assessment that targets the distribution, state and trends of pressures and impacts on key animal and plant biodiversity hosted by wetland habitats in the Mediterranean region. The assessment of wetland biodiversity conditions aims to complement existing knowledge and address the lack of readily available spatially-explicit information on the areas where biodiversity unique to the Mediterranean occurs, and where endemic biodiversity is most threatened, using data from The Red List of Threatened Species™ of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). For the threatened species analysis, only species categorised in the IUCN Red List as Critically Endangered (CR), Endangered (EN) and Vulnerable (VU) were considered. The goal is to highlight priority areas for potential conservation actions in the region, and to support the regional efforts in advocating for effective wetland management and nature-based solutions in the Mediterranean region.
-
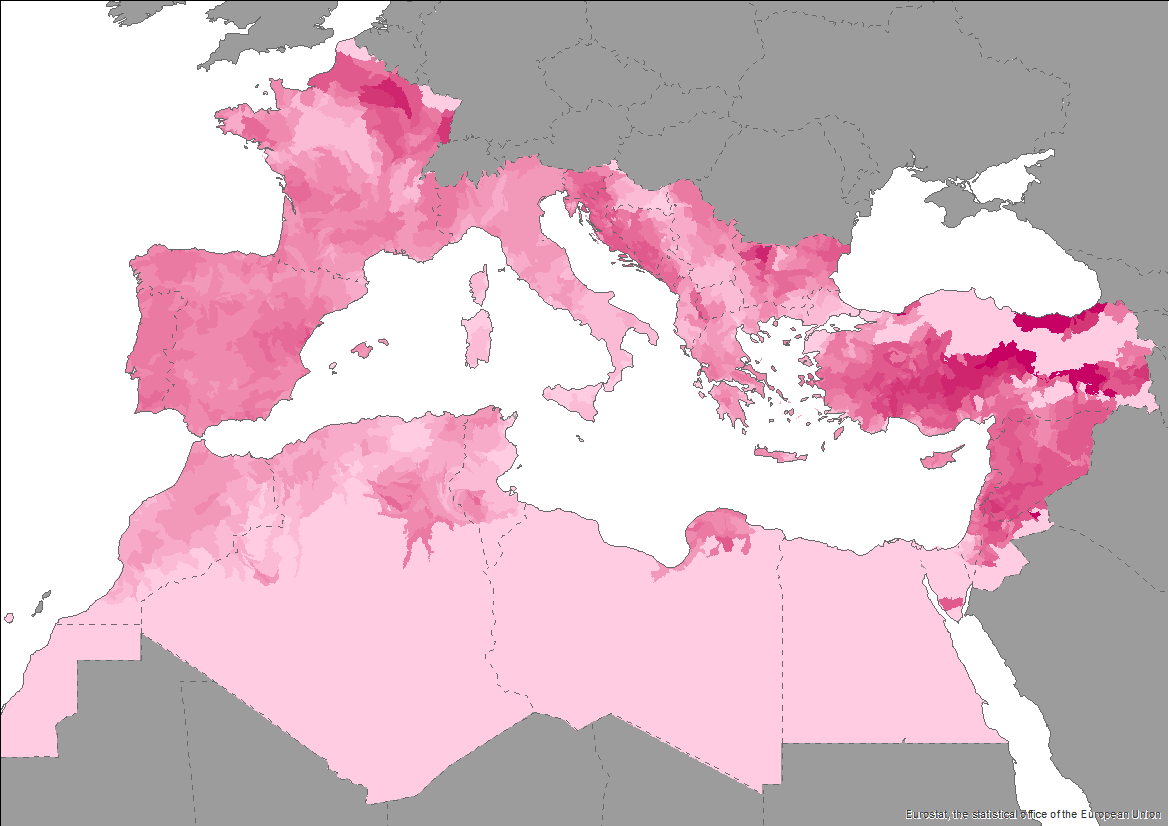
The Pan-Mediterranean wetland knowledge base builds on methods and approaches developed in the framework of on-going efforts at the Mediterranean scale to map wetland ecosystems and assess their condition. It is relevant for several on-going initiatives at a regional, European and global level (e.g. UN Decade on Ecosystem restoration, EU Biodiversity Strategy for 2030, the Barcelona Convention and its protocols on Integrated Coastal Zone Management and Specially Protected Areas). As part of these efforts, ETC-UMA produced an assessment that targets the distribution, state and trends of pressures and impacts on key animal and plant biodiversity hosted by wetland habitats in the Mediterranean region. The assessment of wetland biodiversity conditions aims to complement existing knowledge and address the lack of readily available spatially-explicit information on the areas where biodiversity unique to the Mediterranean occurs, and where endemic biodiversity is most threatened, using data from The Red List of Threatened Species™ of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). For the threatened species analysis, only species categorised in the IUCN Red List as Critically Endangered (CR), Endangered (EN) and Vulnerable (VU) were considered. The goal is to highlight priority areas for potential conservation actions in the region, and to support the regional efforts in advocating for effective wetland management and nature-based solutions in the Mediterranean region.
