Keyword
impact source
49 record(s)
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Status
Scale
panaceaKeywords
GEMET keywords
-
Medbiolitter database summarises results of scientific studies on biodiversity and marine litter interactions in the Mediterranean Sea. To this end, information is collected from different data sources, such as institutions or projects, as well as peer-reviewed publications. The main source of data currently is LITTERBASE/AWI, including only the coverage within the Mediterranean. The database currently comprises 393 records on interactions. Interaction refers to encounters between wildlife and litter items and are classified in four categories: 1) Ingestion, which is the most frequently observed interaction, followed by 2) entanglement, which affects motility, often with fatal consequences, 3) colonization, which occurs when many species settle on floating litter, and 4) others, including different types of less frequent interaction. The database includes among others the location, the type of interaction and litter, marine realm (beach, sea surface, water column, seafloor), habitat, species, whether it occurs in a marine protected area and the type in such case, as well as references to the publication from which the data are extracted. The layer is represented in different ways in the MED Biodiversity platform: 1) Marine litter and biodiversity interactions: it shows the database by type of interaction (ingestion, entanglement, colonization and other) and marine realm (pelagic or benthic). 2) Knowledge update from Nov 2008: changes in the number of records since the last update. It tries to represent the efforts of the PANACeA project to gather additional information on the Mediterranean Sea. 3) Marine litter knowledge from 1988 to 2019: shows the years of publication of the source of the records in the database. In recent dates, especially since 2015, there has been a notable increase in the number of publications related to marine litter.
-
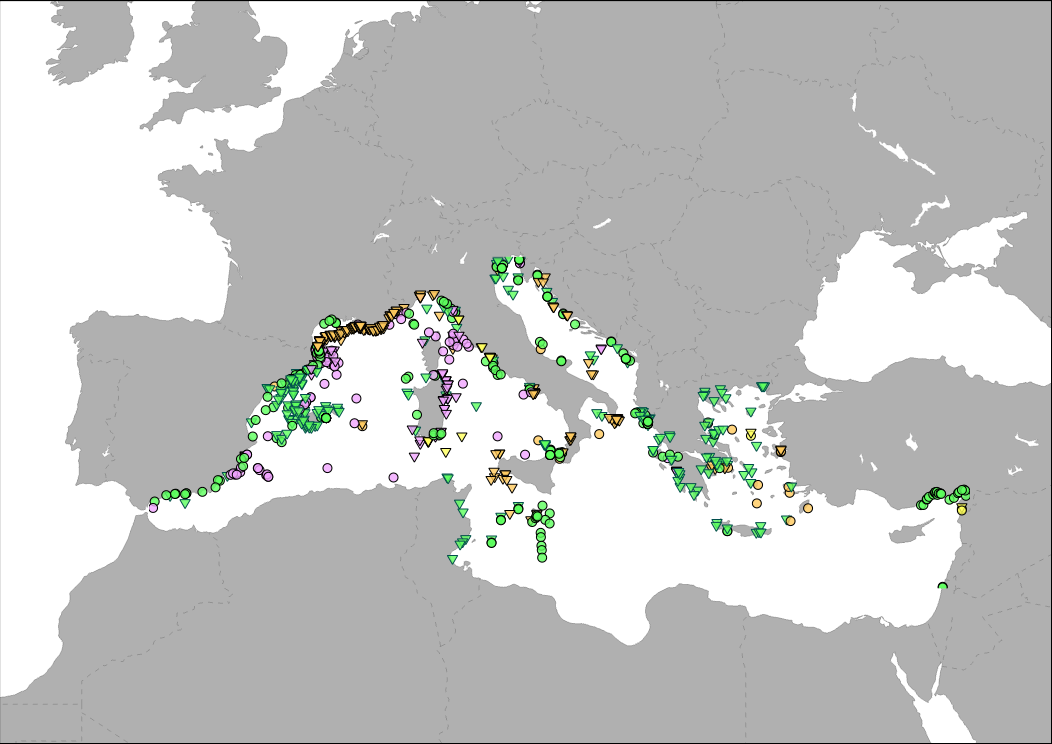
Medbiolitter database summarises results of scientific studies on biodiversity and marine litter interactions in the Mediterranean Sea. To this end, information is collected from different data sources, such as institutions or projects, as well as peer-reviewed publications. One of the main sources of data is LITTERBASE/AWI, only including the coverage within the Mediterranean Sea. The database currently comprises 1056 records on interactions. Interaction refers to encounters between wildlife and litter items and are classified in four categories: 1) Ingestion, which is the most frequently observed interaction, followed by 2) entanglement, which affects motility, often with fatal consequences, 3) colonization, which occurs when many species settle on floating litter, and 4) others, including different types of less frequent interaction. The database includes among others the location, the type of interaction and litter, marine realm (beach, sea surface, water column, seafloor), habitat, species, whether it occurs in a marine protected area and the type in such case, as well as references to the publication from which the data are extracted.
-
Medbiolitter database summarises results of scientific studies on biodiversity and marine litter interactions in the Mediterranean Sea. To this end, information is collected from different data sources, such as institutions or projects, as well as peer-reviewed publications. The main source of data currently is LITTERBASE/AWI, including only the coverage within the Mediterranean. The database currently comprises 393 records on interactions. Interaction refers to encounters between wildlife and litter items and are classified in four categories: 1) Ingestion, which is the most frequently observed interaction, followed by 2) entanglement, which affects motility, often with fatal consequences, 3) colonization, which occurs when many species settle on floating litter, and 4) others, including different types of less frequent interaction. The database includes among others the location, the type of interaction and litter, marine realm (beach, sea surface, water column, seafloor), habitat, species, whether it occurs in a marine protected area and the type in such case, as well as references to the publication from which the data are extracted. The layer is represented in different ways in the MED Biodiversity platform: 1) Marine litter and biodiversity interactions: it shows the database by type of interaction (ingestion, entanglement, colonization and other) and marine realm (pelagic or benthic). 2) Knowledge update from Nov 2008: changes in the number of records since the last update. It tries to represent the efforts of the PANACeA project to gather additional information on the Mediterranean Sea. 3) Marine litter knowledge from 1988 to 2019: shows the years of publication of the source of the records in the database. In recent dates, especially since 2015, there has been a notable increase in the number of publications related to marine litter.
-
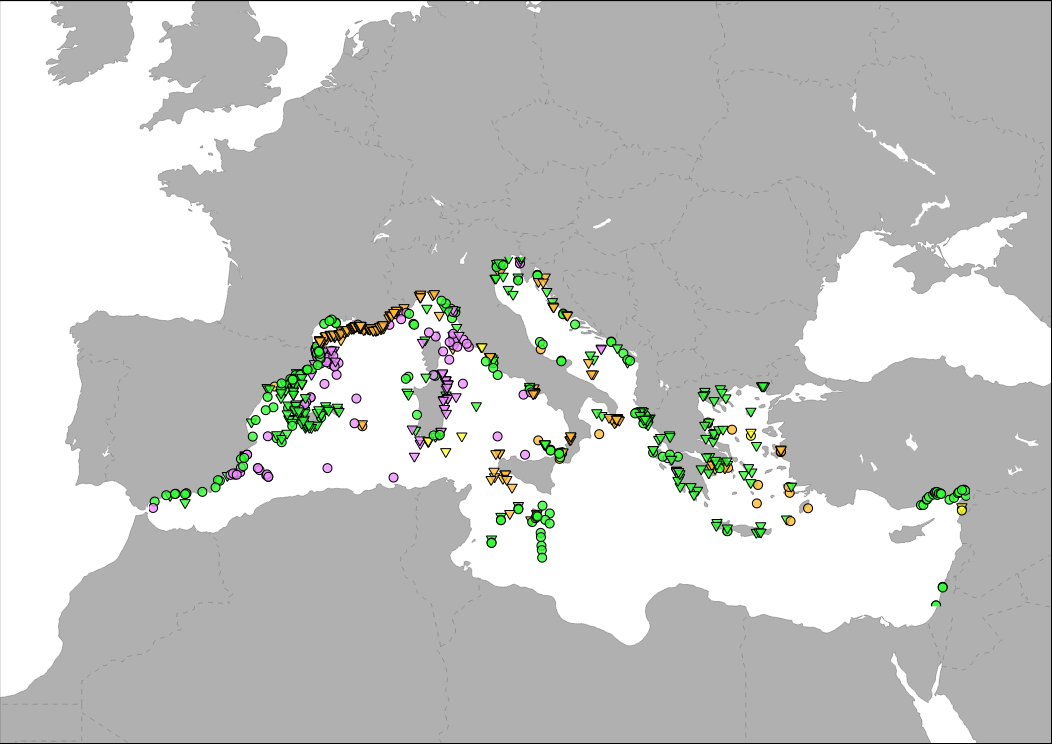
Medbiolitter database summarises results of scientific studies on biodiversity and marine litter interactions in the Mediterranean Sea. To this end, information is collected from different data sources, such as institutions or projects, as well as peer-reviewed publications. The main source of data currently is LITTERBASE/AWI, including only the coverage within the Mediterranean. The database currently comprises 754 records on interactions. Interaction refers to encounters between wildlife and litter items and are classified in four categories: 1) Ingestion, which is the most frequently observed interaction, followed by 2) entanglement, which affects motility, often with fatal consequences, 3) colonization, which occurs when many species settle on floating litter, and 4) others, including different types of less frequent interaction. The database includes among others the location, the type of interaction and litter, marine realm (beach, sea surface, water column, seafloor), habitat, species, whether it occurs in a marine protected area and the type in such case, as well as references to the publication from which the data are extracted. The layer is represented in different ways in the MED Biodiversity platform: 1) Marine litter and biodiversity interactions: it shows the database by type of interaction (ingestion, entanglement, colonization and other) and marine realm (pelagic or benthic). 2) Knowledge update: changes in the number of records in each database version. It tries to represent the efforts of the PANACeA project to gather additional information on the Mediterranean Sea. 3) Marine litter knowledge from 1988 to present date: shows the years of publication of the source of the records in the database. In recent dates, especially since 2015, there has been a notable increase in the number of publications related to marine litter.
-
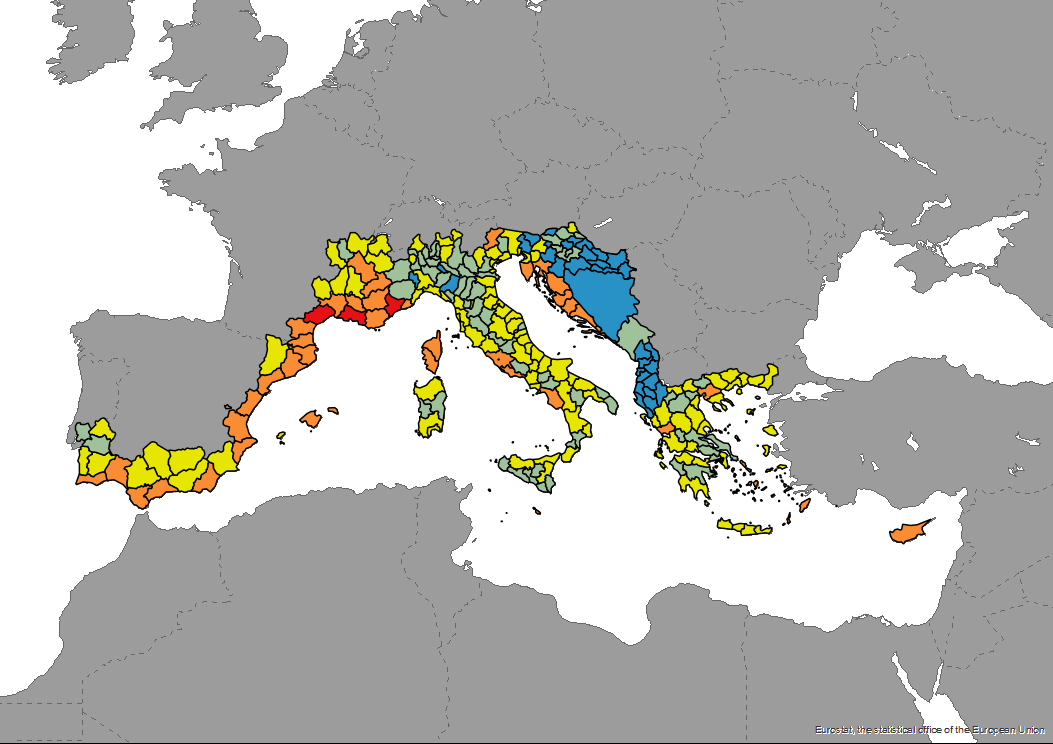
The dataset of the ecological vulnerability to tourism by NUTS3 areas is produced in the framework of DestiMED PLUS. DestiMED PLUS Project builds on the successes of MEET and DestiMED projects and aims to improve levels of integration between regional tourism and conservation policies in the protected areas of 9 Mediterranean Regions through the creation of ecotourism itineraries which are developed using a collaborative approach, both locally and regionally to develop ecotourism.
-
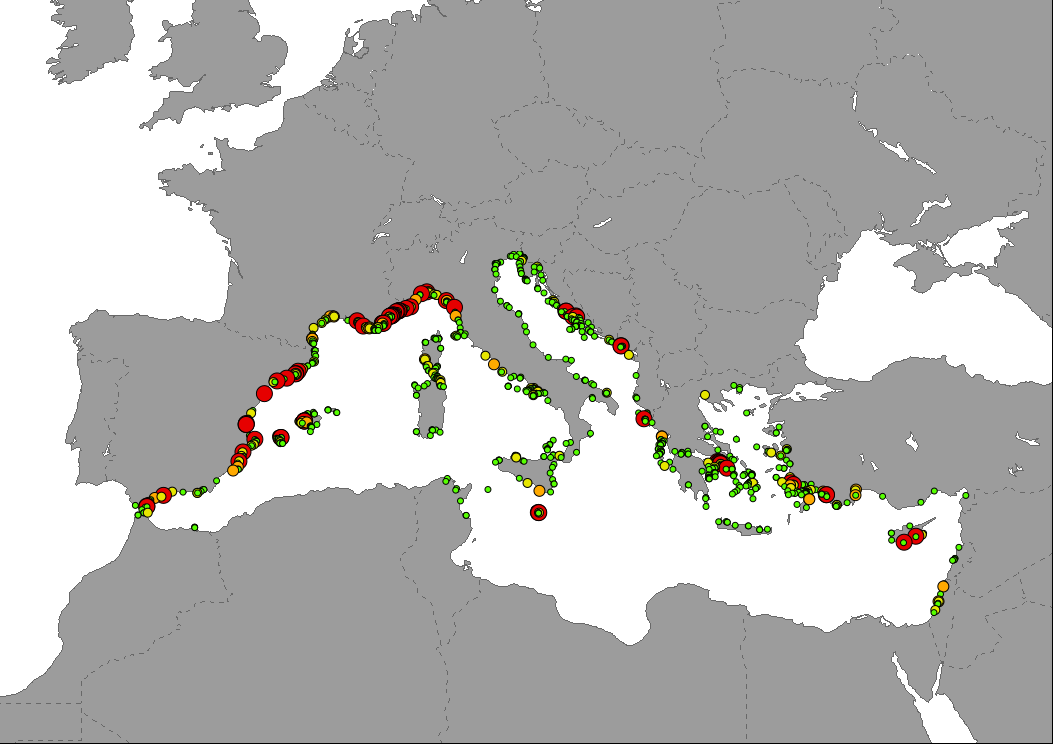
Data representing the cumulative tourism pressure in Mediterranean Sea waters based on the intensity of maritime traffic of passengers vessels and pleasure craft. Traffic intensity was produced using AIS data aggregated at 1km2 by EMODnet and expressed as total time with presence of vessels in each cell throughout the year (hours/km2). Pressure hotspots are highlighted on the map, being classified as: 1) low; areas with cumulative presence of vessels from one hour a day to 4 months (1 quarter); 2) moderate; areas with cumulative presence of vessels between 4 and 8 months (1 to 2 quarters); 3) high, areas with cumulative presence of vessels between 8 months (2 quarters) and one year; 4) very high, areas where there is a cumulative presence of vessels exciding one year, being locations of very high traffic intensity.
-
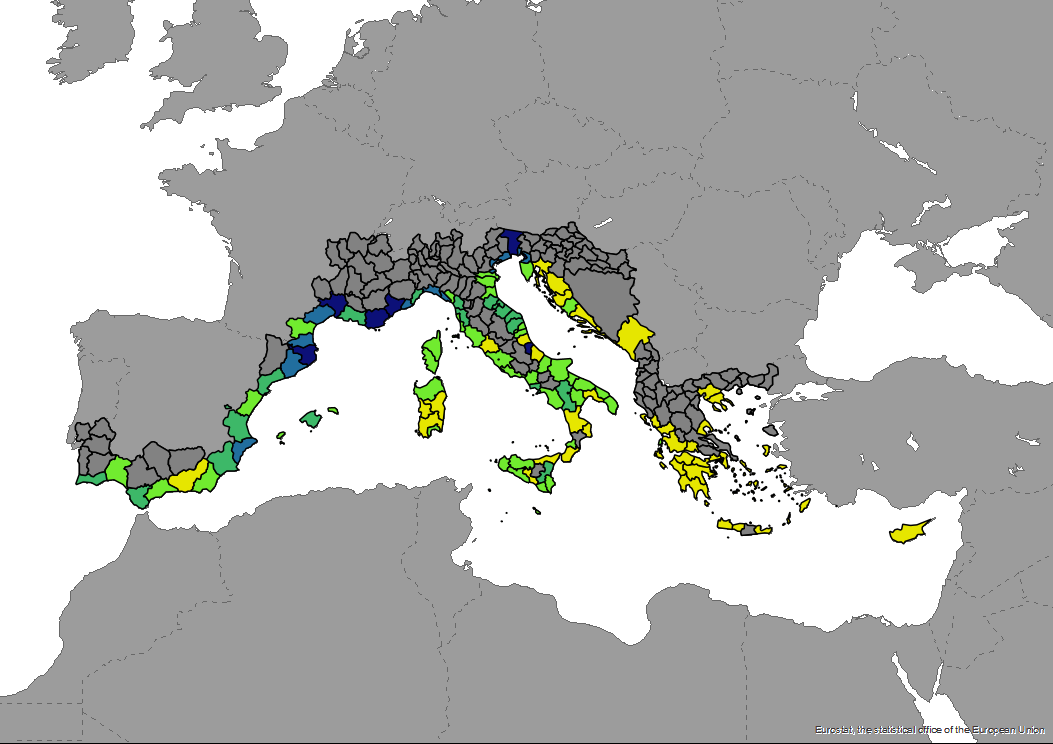
The dataset of the number of moorings in marina ports per kilometre of coastline for each NUTS3 region, based on Portbooker.com, 2022 is produced in the framework of DestiMED PLUS. DestiMED PLUS Project builds on the successes of MEET and DestiMED projects and aims to improve levels of integration between regional tourism and conservation policies in the protected areas of 9 Mediterranean Regions through the creation of ecotourism itineraries which are developed using a collaborative approach, both locally and regionally to develop ecotourism.
-
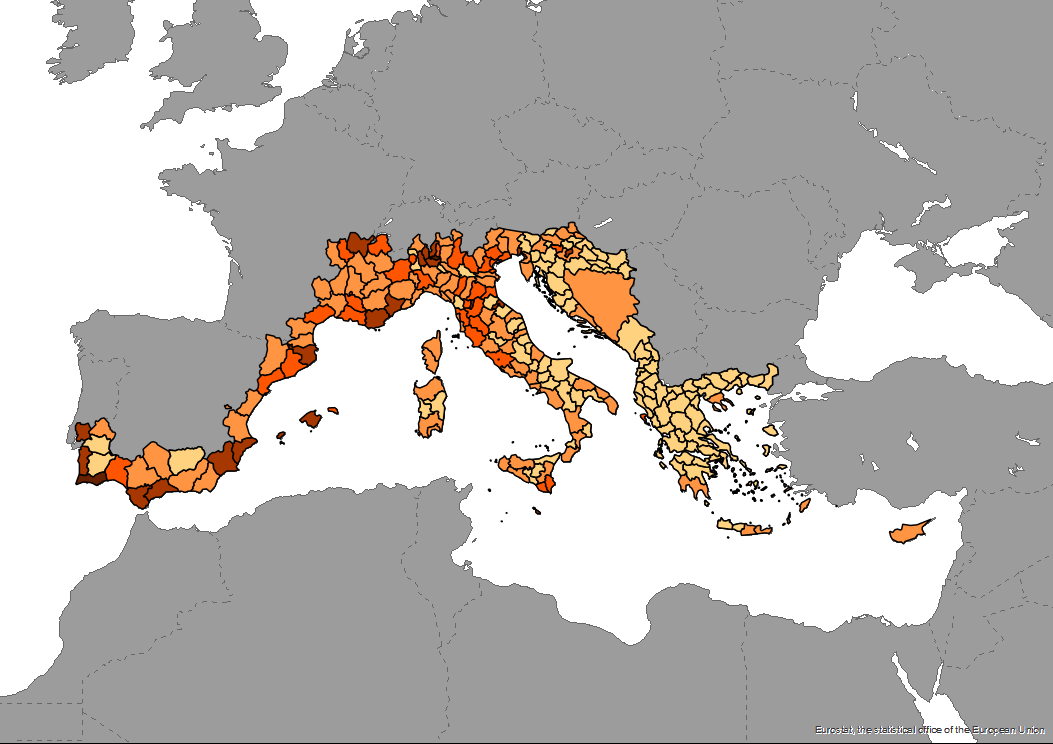
The dataset of the number of bed places in coastal and non-coastal areas per km2, as an indicator of the local intensity of tourism capacity is produced in the framework of DestiMED PLUS. DestiMED PLUS Project builds on the successes of MEET and DestiMED projects and aims to improve levels of integration between regional tourism and conservation policies in the protected areas of 9 Mediterranean Regions through the creation of ecotourism itineraries which are developed using a collaborative approach, both locally and regionally to develop ecotourism.
-
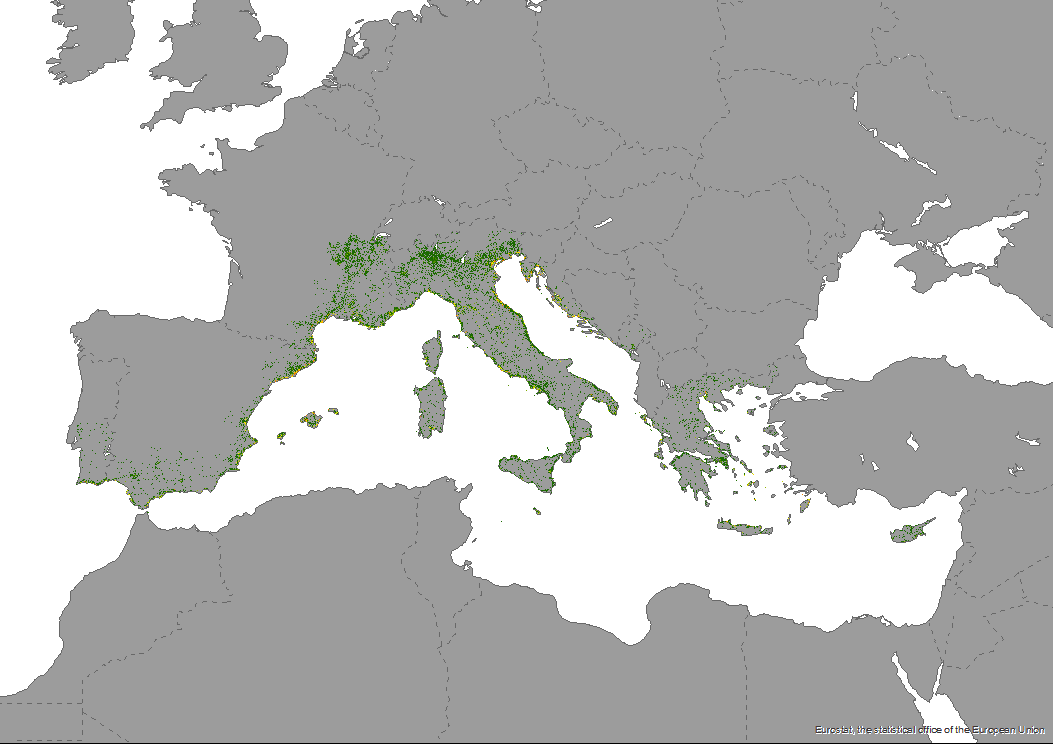
The dataset of the surface percentage occupied by golf courses in NUTS3 as a proxy for the potential environmental pressure of this tourist activity is produced in the framework of DestiMED PLUS. DestiMED PLUS Project builds on the successes of MEET and DestiMED projects and aims to improve levels of integration between regional tourism and conservation policies in the protected areas of 9 Mediterranean Regions through the creation of ecotourism itineraries which are developed using a collaborative approach, both locally and regionally to develop ecotourism.
-

The dataset of the number of nights spent by tourists in coastal and non-coastal areas per km2, as an indicator of the local intensity of tourism capacity is produced in the framework of DestiMED PLUS. DestiMED PLUS Project builds on the successes of MEET and DestiMED projects and aims to improve levels of integration between regional tourism and conservation policies in the protected areas of 9 Mediterranean Regions through the creation of ecotourism itineraries which are developed using a collaborative approach, both locally and regionally to develop ecotourism.
