Keyword
litter
19 record(s)
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Status
Service types
Scale
panaceaKeywords
GEMET keywords
-
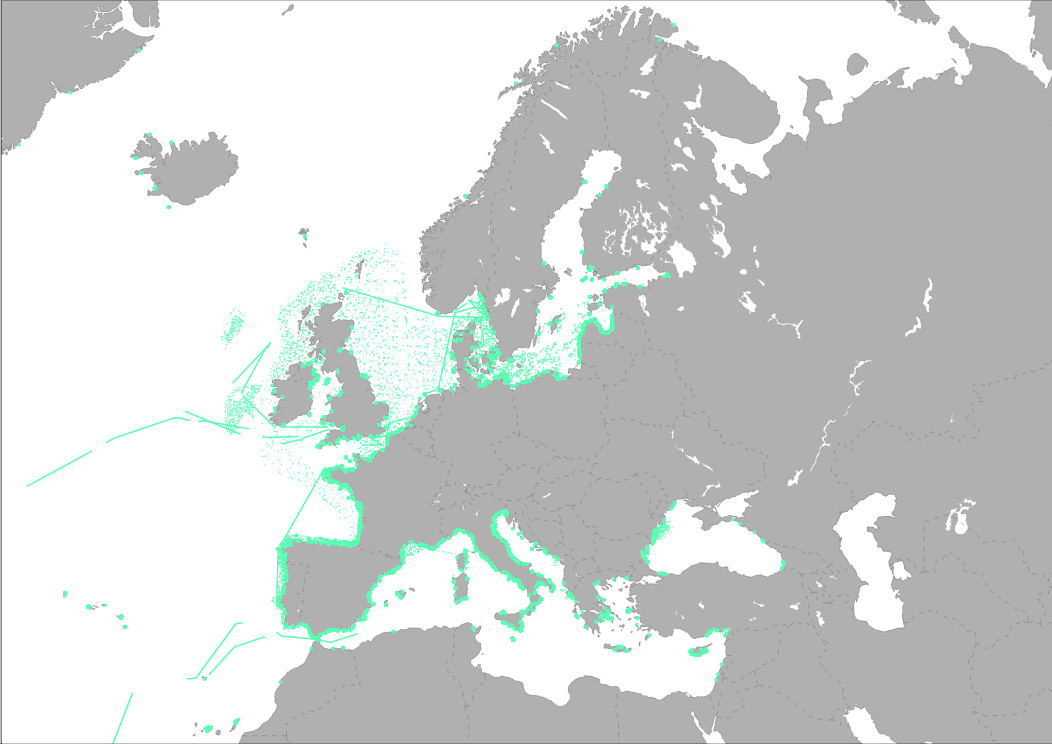
EMODnet Chemistry aims to provide access to marine chemistry data sets and derived data products concerning eutrophication, ocean acidification, contaminants and litter. The chosen parameters are relevant for the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD), in particular for descriptors 5, 8, 9 and 10. The dataset contains standardized, harmonized and validated data collections from beach litter (monitoring and other sources)..
-
Transborder Fix line transect are used to assess amount, composition, and spatial distribution of floating macro litter, bigger than 20 cm, along fixed trans-border transects in the Mediterranean basin. The transects, monitored all year round, cross the south east partof Ligurian Sea, Sardinian Balearic basin, Bonifacio Strait, Central Tyrrhenian Sea, Sicilian Sardinian Channels, Adriatic Sea , and Ionian Sea. The surveyed area en-compasses a large portion of the Mediterranean Sea and falls withinthree MSFD marine subregions: the Western Mediterranean Sea, theAdriatic Sea, the Ionian and Central Mediterranean Sea.
-
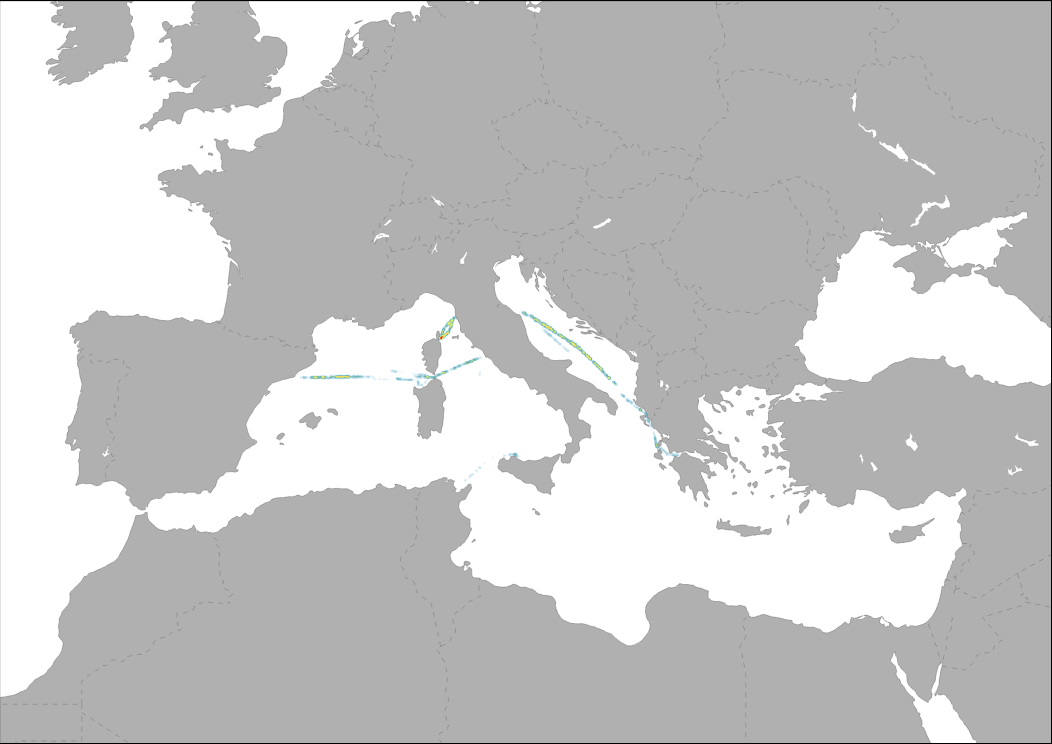
Transborder Fix line transect are used to assess amount, composition, and spatial distribution of floating macro litter, bigger than 20 cm, along fixed trans-border transects in the Mediterranean basin. The transects, monitored all year round, cross the south east partof Ligurian Sea, Sardinian Balearic basin, Bonifacio Strait, Central Tyrrhenian Sea, Sicilian Sardinian Channels, Adriatic Sea , and Ionian Sea. The surveyed area en-compasses a large portion of the Mediterranean Sea and falls withinthree MSFD marine subregions: the Western Mediterranean Sea, theAdriatic Sea, the Ionian and Central Mediterranean Sea.
-
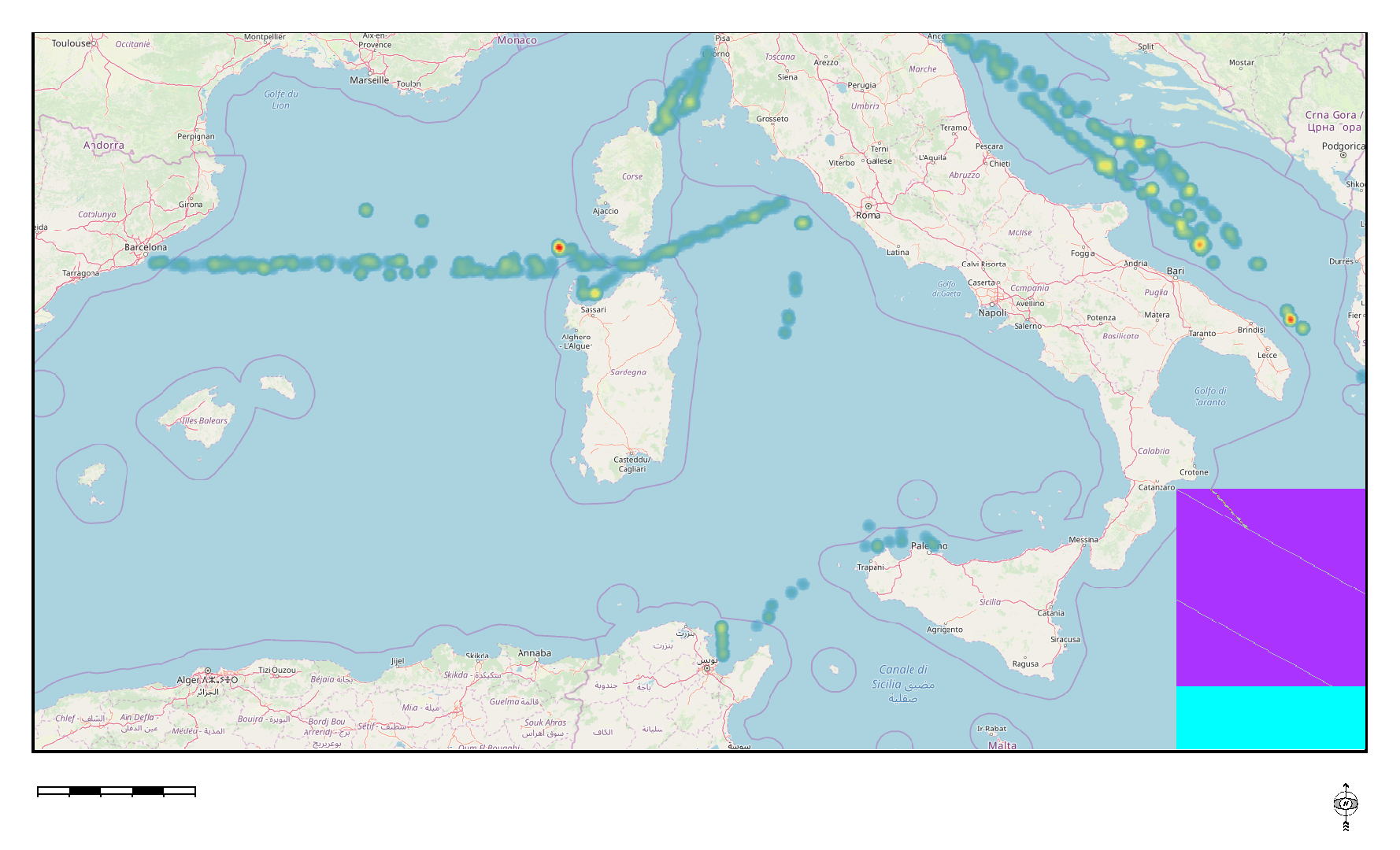
Transborder Fix line transects are used by the MedSeaLitter project to assess the amount, composition, and spatial distribution of floating macro litter, bigger than 20 cm, in the Mediterranean basin. The transects, monitored all year round, cross the south east part of the Ligurian Sea, Sardinian Balearic basin, Bonifacio Strait, Central Tyrrhenian Sea, Sicilian Sardinian Channels, Adriatic Sea, and Ionian Sea. The surveyed area en-compasses a large portion of the Mediterranean Sea and falls within the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) marine sub-regions: the Western Mediterranean Sea, the Adriatic Sea, the Ionian and Central Mediterranean Sea.
-
Transborder Fix line transect are used to assess amount, composition, and spatial distribution of floating macro litter, bigger than 20 cm, along fixed trans-border transects in the Mediterranean basin. The transects, monitored all year round, cross the south east partof Ligurian Sea, Sardinian Balearic basin, Bonifacio Strait, Central Tyrrhenian Sea, Sicilian Sardinian Channels, Adriatic Sea , and Ionian Sea. The surveyed area en-compasses a large portion of the Mediterranean Sea and falls withinthree MSFD marine subregions: the Western Mediterranean Sea, theAdriatic Sea, the Ionian and Central Mediterranean Sea.
-
Medbiolitter database summarises results of scientific studies on biodiversity and marine litter interactions in the Mediterranean Sea. To this end, information is collected from different data sources, such as institutions or projects, as well as peer-reviewed publications. The main source of data currently is LITTERBASE/AWI, including only the coverage within the Mediterranean. The database currently comprises 393 records on interactions. Interaction refers to encounters between wildlife and litter items and are classified in four categories: 1) Ingestion, which is the most frequently observed interaction, followed by 2) entanglement, which affects motility, often with fatal consequences, 3) colonization, which occurs when many species settle on floating litter, and 4) others, including different types of less frequent interaction. The database includes among others the location, the type of interaction and litter, marine realm (beach, sea surface, water column, seafloor), habitat, species, whether it occurs in a marine protected area and the type in such case, as well as references to the publication from which the data are extracted. The layer is represented in different ways in the MED Biodiversity platform: 1) Marine litter and biodiversity interactions: it shows the database by type of interaction (ingestion, entanglement, colonization and other) and marine realm (pelagic or benthic). 2) Knowledge update from Nov 2008: changes in the number of records since the last update. It tries to represent the efforts of the PANACeA project to gather additional information on the Mediterranean Sea. 3) Marine litter knowledge from 1988 to 2019: shows the years of publication of the source of the records in the database. In recent dates, especially since 2015, there has been a notable increase in the number of publications related to marine litter.
-
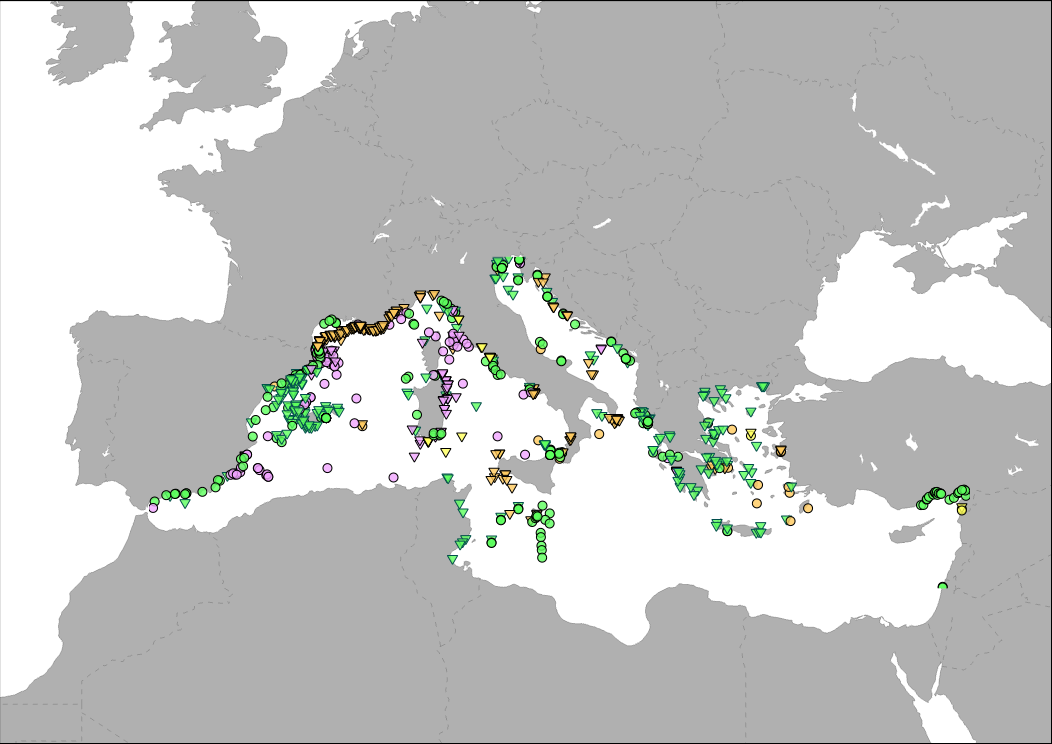
Medbiolitter database summarises results of scientific studies on biodiversity and marine litter interactions in the Mediterranean Sea. To this end, information is collected from different data sources, such as institutions or projects, as well as peer-reviewed publications. One of the main sources of data is LITTERBASE/AWI, only including the coverage within the Mediterranean Sea. The database currently comprises 1056 records on interactions. Interaction refers to encounters between wildlife and litter items and are classified in four categories: 1) Ingestion, which is the most frequently observed interaction, followed by 2) entanglement, which affects motility, often with fatal consequences, 3) colonization, which occurs when many species settle on floating litter, and 4) others, including different types of less frequent interaction. The database includes among others the location, the type of interaction and litter, marine realm (beach, sea surface, water column, seafloor), habitat, species, whether it occurs in a marine protected area and the type in such case, as well as references to the publication from which the data are extracted.
-
Medbiolitter database summarises results of scientific studies on biodiversity and marine litter interactions in the Mediterranean Sea. To this end, information is collected from different data sources, such as institutions or projects, as well as peer-reviewed publications. The main source of data currently is LITTERBASE/AWI, including only the coverage within the Mediterranean. The database currently comprises 393 records on interactions. Interaction refers to encounters between wildlife and litter items and are classified in four categories: 1) Ingestion, which is the most frequently observed interaction, followed by 2) entanglement, which affects motility, often with fatal consequences, 3) colonization, which occurs when many species settle on floating litter, and 4) others, including different types of less frequent interaction. The database includes among others the location, the type of interaction and litter, marine realm (beach, sea surface, water column, seafloor), habitat, species, whether it occurs in a marine protected area and the type in such case, as well as references to the publication from which the data are extracted. The layer is represented in different ways in the MED Biodiversity platform: 1) Marine litter and biodiversity interactions: it shows the database by type of interaction (ingestion, entanglement, colonization and other) and marine realm (pelagic or benthic). 2) Knowledge update from Nov 2008: changes in the number of records since the last update. It tries to represent the efforts of the PANACeA project to gather additional information on the Mediterranean Sea. 3) Marine litter knowledge from 1988 to 2019: shows the years of publication of the source of the records in the database. In recent dates, especially since 2015, there has been a notable increase in the number of publications related to marine litter.
-
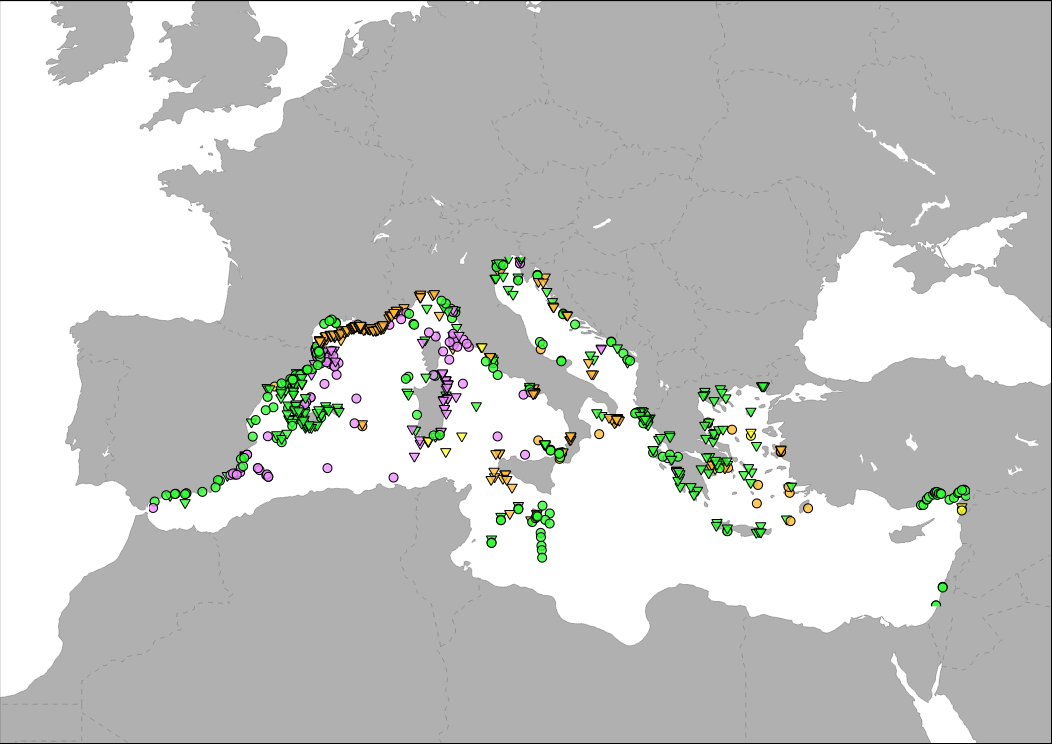
Medbiolitter database summarises results of scientific studies on biodiversity and marine litter interactions in the Mediterranean Sea. To this end, information is collected from different data sources, such as institutions or projects, as well as peer-reviewed publications. The main source of data currently is LITTERBASE/AWI, including only the coverage within the Mediterranean. The database currently comprises 754 records on interactions. Interaction refers to encounters between wildlife and litter items and are classified in four categories: 1) Ingestion, which is the most frequently observed interaction, followed by 2) entanglement, which affects motility, often with fatal consequences, 3) colonization, which occurs when many species settle on floating litter, and 4) others, including different types of less frequent interaction. The database includes among others the location, the type of interaction and litter, marine realm (beach, sea surface, water column, seafloor), habitat, species, whether it occurs in a marine protected area and the type in such case, as well as references to the publication from which the data are extracted. The layer is represented in different ways in the MED Biodiversity platform: 1) Marine litter and biodiversity interactions: it shows the database by type of interaction (ingestion, entanglement, colonization and other) and marine realm (pelagic or benthic). 2) Knowledge update: changes in the number of records in each database version. It tries to represent the efforts of the PANACeA project to gather additional information on the Mediterranean Sea. 3) Marine litter knowledge from 1988 to present date: shows the years of publication of the source of the records in the database. In recent dates, especially since 2015, there has been a notable increase in the number of publications related to marine litter.
-
Transborder Fix line transects are used by the MedSeaLitter project to assess the amount, composition, and spatial distribution of floating macro litter, bigger than 20 cm, in the Mediterranean basin. The transects, monitored all year round, cross the south east part of the Ligurian Sea, Sardinian Balearic basin, Bonifacio Strait, Central Tyrrhenian Sea, Sicilian Sardinian Channels, Adriatic Sea, and Ionian Sea. The surveyed area en-compasses a large portion of the Mediterranean Sea and falls within the MSFD marine sub-regions: the Western Mediterranean Sea, the Adriatic Sea, the Ionian and Central Mediterranean Sea.
