Keyword
marine pollution
8 record(s)
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Status
Scale
panaceaKeywords
GEMET keywords
-
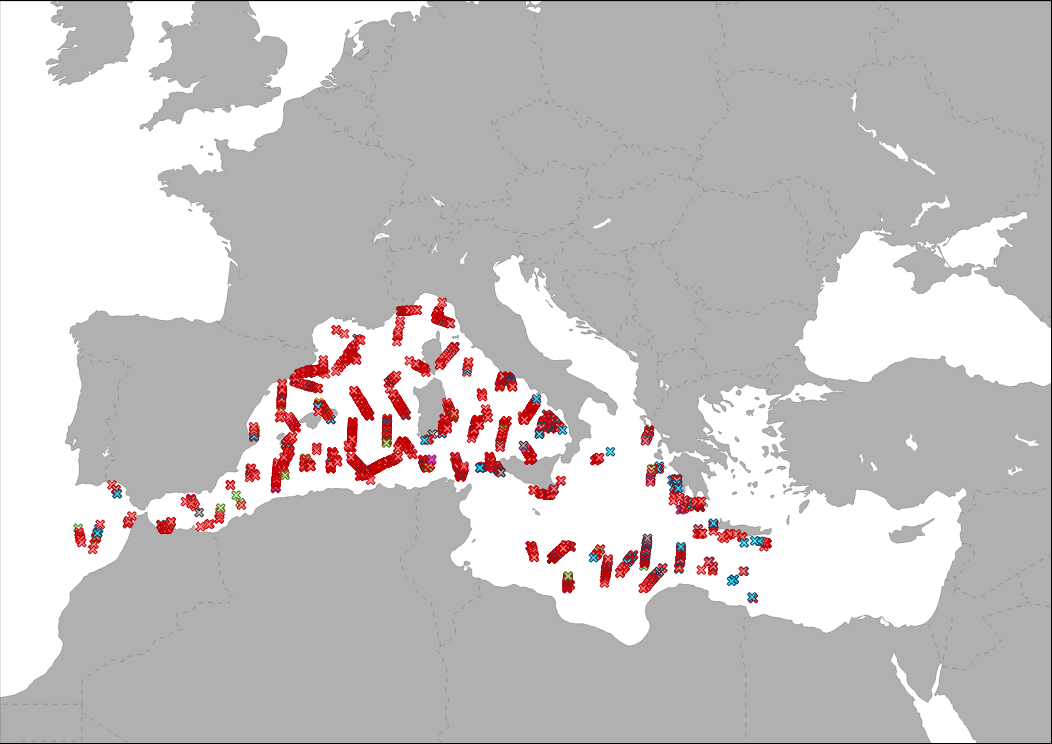
The data collected by a vessel survey organized within the ACCOBAMS agreement, is showing by point different floating rubbish identified during the ACCOBAMS Survey Initiative (ASI) along the Mediterranean Sea.
-
Transborder Fix line transect are used to assess amount, composition, and spatial distribution of floating macro litter, bigger than 20 cm, along fixed trans-border transects in the Mediterranean basin. The transects, monitored all year round, cross the south east partof Ligurian Sea, Sardinian Balearic basin, Bonifacio Strait, Central Tyrrhenian Sea, Sicilian Sardinian Channels, Adriatic Sea , and Ionian Sea. The surveyed area en-compasses a large portion of the Mediterranean Sea and falls withinthree MSFD marine subregions: the Western Mediterranean Sea, theAdriatic Sea, the Ionian and Central Mediterranean Sea.
-
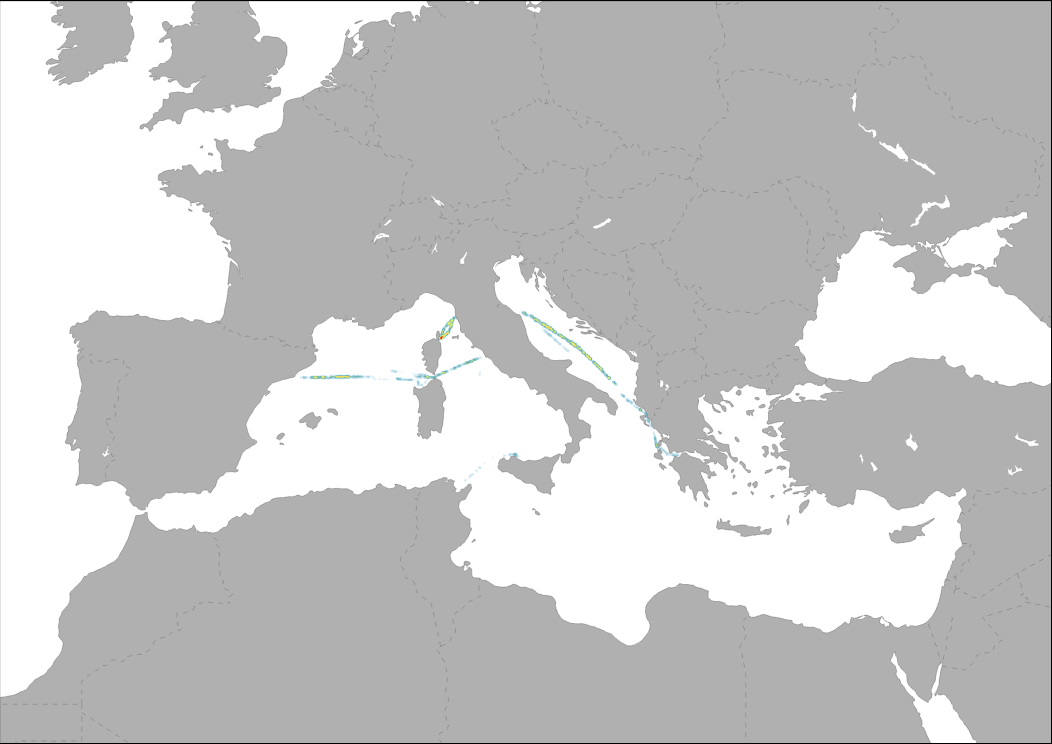
Transborder Fix line transect are used to assess amount, composition, and spatial distribution of floating macro litter, bigger than 20 cm, along fixed trans-border transects in the Mediterranean basin. The transects, monitored all year round, cross the south east partof Ligurian Sea, Sardinian Balearic basin, Bonifacio Strait, Central Tyrrhenian Sea, Sicilian Sardinian Channels, Adriatic Sea , and Ionian Sea. The surveyed area en-compasses a large portion of the Mediterranean Sea and falls withinthree MSFD marine subregions: the Western Mediterranean Sea, theAdriatic Sea, the Ionian and Central Mediterranean Sea.
-
Transborder Fix line transects are used by the MedSeaLitter project to assess the amount, composition, and spatial distribution of floating macro litter, bigger than 20 cm, in the Mediterranean basin. The transects, monitored all year round, cross the south east part of the Ligurian Sea, Sardinian Balearic basin, Bonifacio Strait, Central Tyrrhenian Sea, Sicilian Sardinian Channels, Adriatic Sea, and Ionian Sea. The surveyed area en-compasses a large portion of the Mediterranean Sea and falls within the Marine Strategy Framework Directive (MSFD) marine sub-regions: the Western Mediterranean Sea, the Adriatic Sea, the Ionian and Central Mediterranean Sea.
-
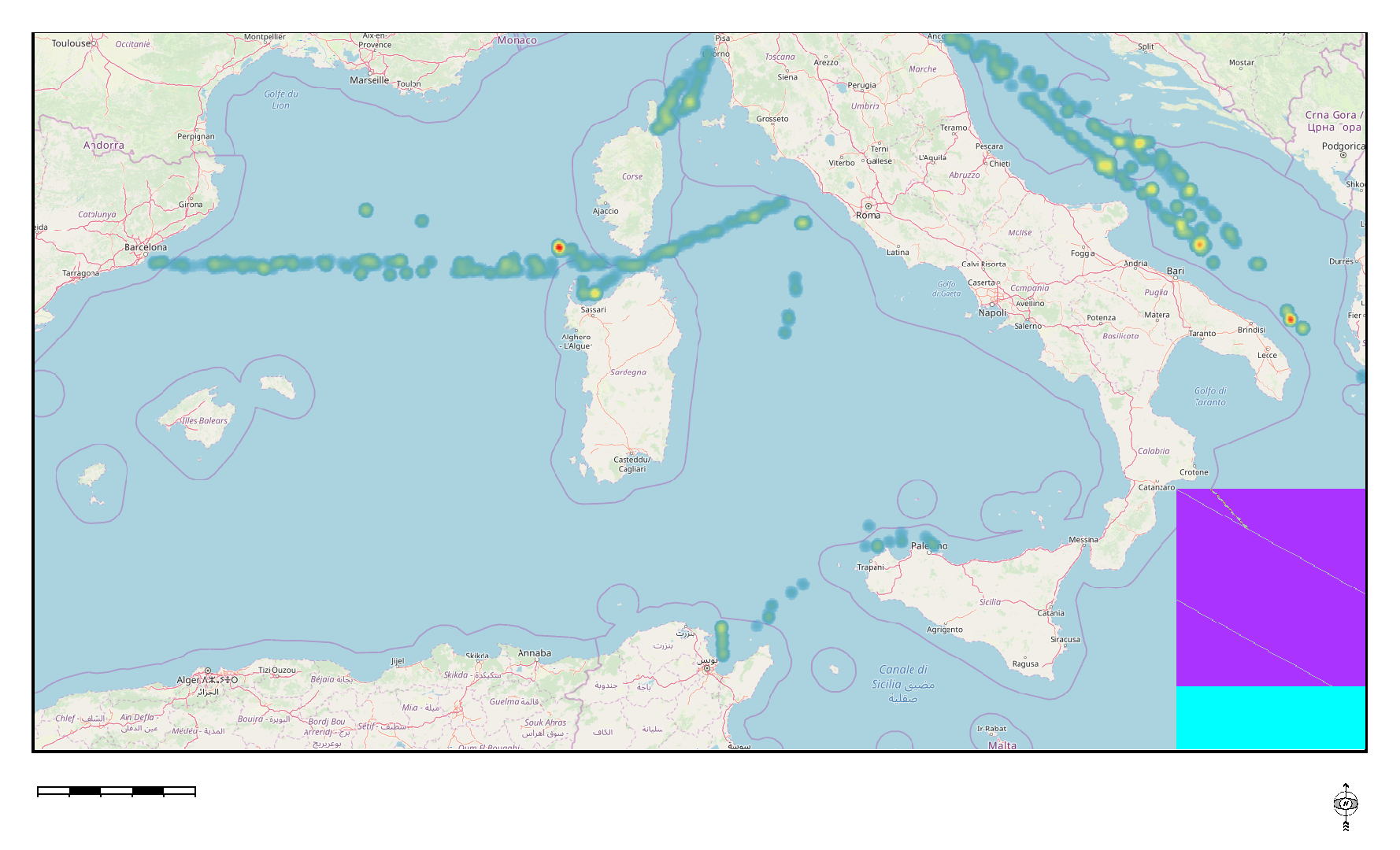
Transborder Fix line transect are used to assess amount, composition, and spatial distribution of floating macro litter, bigger than 20 cm, along fixed trans-border transects in the Mediterranean basin. The transects, monitored all year round, cross the south east partof Ligurian Sea, Sardinian Balearic basin, Bonifacio Strait, Central Tyrrhenian Sea, Sicilian Sardinian Channels, Adriatic Sea , and Ionian Sea. The surveyed area en-compasses a large portion of the Mediterranean Sea and falls withinthree MSFD marine subregions: the Western Mediterranean Sea, theAdriatic Sea, the Ionian and Central Mediterranean Sea.
-
Transborder Fix line transects are used by the MedSeaLitter project to assess the amount, composition, and spatial distribution of floating macro litter, bigger than 20 cm, in the Mediterranean basin. The transects, monitored all year round, cross the south east part of the Ligurian Sea, Sardinian Balearic basin, Bonifacio Strait, Central Tyrrhenian Sea, Sicilian Sardinian Channels, Adriatic Sea, and Ionian Sea. The surveyed area en-compasses a large portion of the Mediterranean Sea and falls within the MSFD marine sub-regions: the Western Mediterranean Sea, the Adriatic Sea, the Ionian and Central Mediterranean Sea.
-
Transborder Fix line transect are used to assess amount, composition, and spatial distribution of floating macro litter, bigger than 20 cm, along fixed trans-border transects in the Mediterranean basin. The transects, monitored all year round, cross the south east partof Ligurian Sea, Sardinian Balearic basin, Bonifacio Strait, Central Tyrrhenian Sea, Sicilian Sardinian Channels, Adriatic Sea , and Ionian Sea. The surveyed area en-compasses a large portion of the Mediterranean Sea and falls withinthree MSFD marine subregions: the Western Mediterranean Sea, theAdriatic Sea, the Ionian and Central Mediterranean Sea.
-
Rivers acts as a pathway for mismanaged waste to reach the sea. Results of the monitoring in the Fiumicino canal (Tiber river-Italy), estimated that 85.4 (± 9.4) litter items get into the sea each hour, with approximately 30% of which were already fragmented. Within the Medsealitter project, a surface density at the river mouth of approximately 1,270 litter items >2.5 cm and 190 litter items >20 cm per km2 was extrapolated. The percentage of the materials found is the following: Artificial polymer materials 82%; Cloth/Textiles 1%; Metal 3%; Paper/Cardboard 8%; Processed/worked wood 1%; Rubber 5%. Study reference: "Down to the river: amount, composition, and economic sector of litter entering the marine compartment, through the Tiber river in the Western Mediterranean Sea." (DOI: 10.1007/s12210-018-0747-y). Rendiconti Lincei. Scienze Fisiche e Naturali
